Outline of LLM acceleration
Summary
Methods
There are two main methods to acclerate LLM and another tricky methods
- low-rank: reduce dimension of matrix
- block: compute matrix with block
- trick: update model structure or change training process
Reference
- xformers: collection of optimized transformers
- unsloth
- triton
- Liger-Kernel
- Flash-attention
- Megatron-LM from NVIDIA
- huggingface accelerate
- ColossalAI
- awesome LLM system
Categories
Low-rank
LoRA
Low-Rank of large matrices when fine-tune
informaiton
- Jun 2021
- 70%
- note
reference
- Measuring the Intrinsic Dimension of Objective Landscapes
- Intrinsic Dimensionality Explains the Effectiveness of Language Model Fine-Tuning
Linformer
SVD decomposition for large QKV projection matrices to reduce required memory
- Jun 2020
- 30%
- code: hold
Performers
low-rank projection with a novel method named FAVOR
- Sep 2020
- 10%
- code: hold
Multi-head Latent Attention
Project high dimension into low dimension for KV cache, which can reduct much memory ustage.
Block
FlashAttention
Matrices multiplication by blocks
Self-attention Does Not Need O(n2) Memory
attention calculation with blocks
- Dec 2021
- 70%
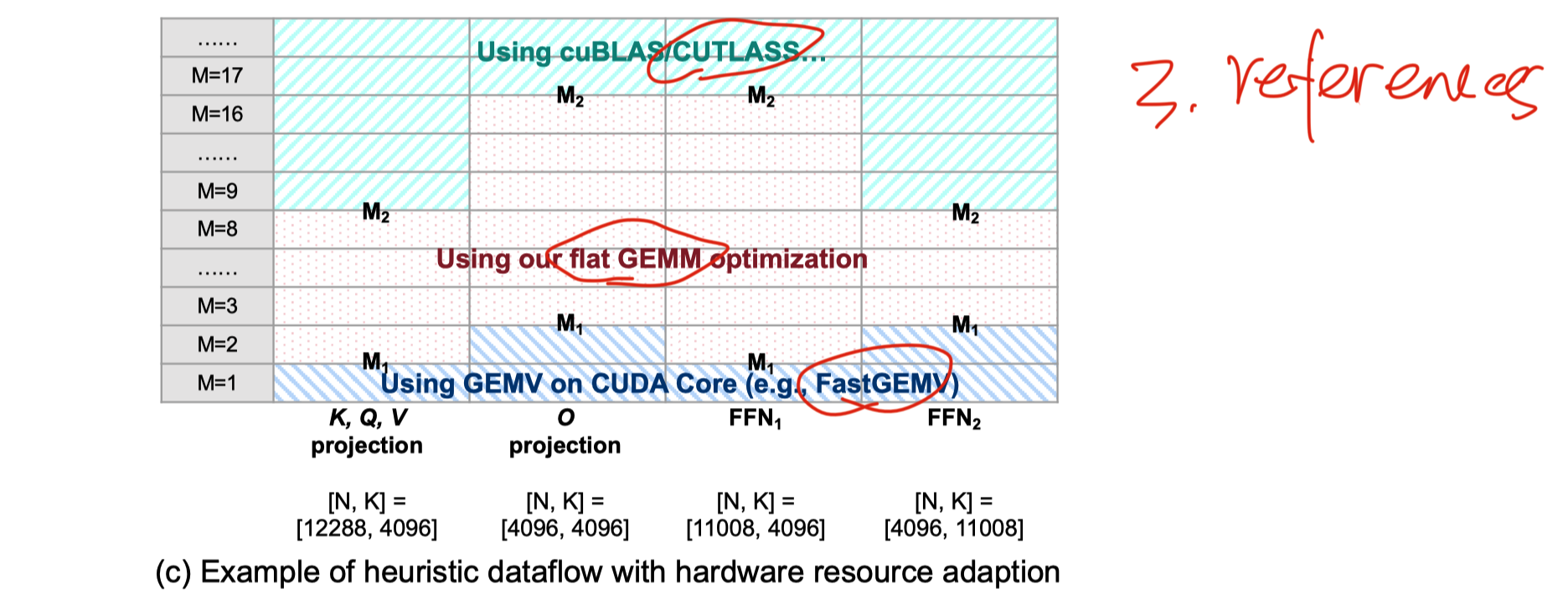
FlashDecoding++
FlashDecoding++: Faster Large Language Model Inference on GPUs, three parts
Softmax with block and Unified Maximum Value, result of block softmax can be directly used and merging is unnecesary. Optimized from FlashAttention.
- Flat GEMM(small batch size when reference) Optimization with Double Buffering. [didn’t understand]
Heuristic Dataflow with Hardware Resource Adaption, choose difference optimizaiton methods for different M value(batch size and sequence length) [didn’t total understand]
- reference
- cuBLAS / CUTLASS
- flat GEMM: method in current paper
- fastGEMV
- No code(2024.11)
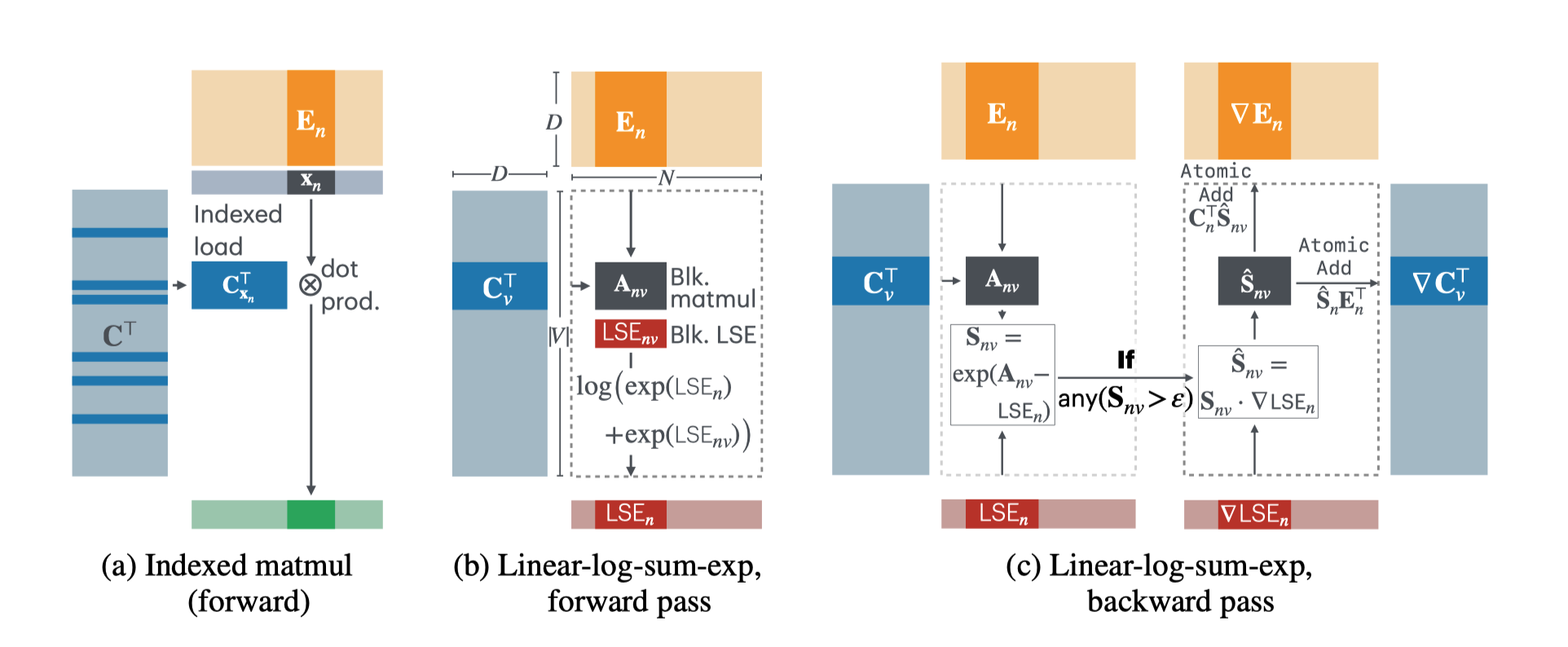
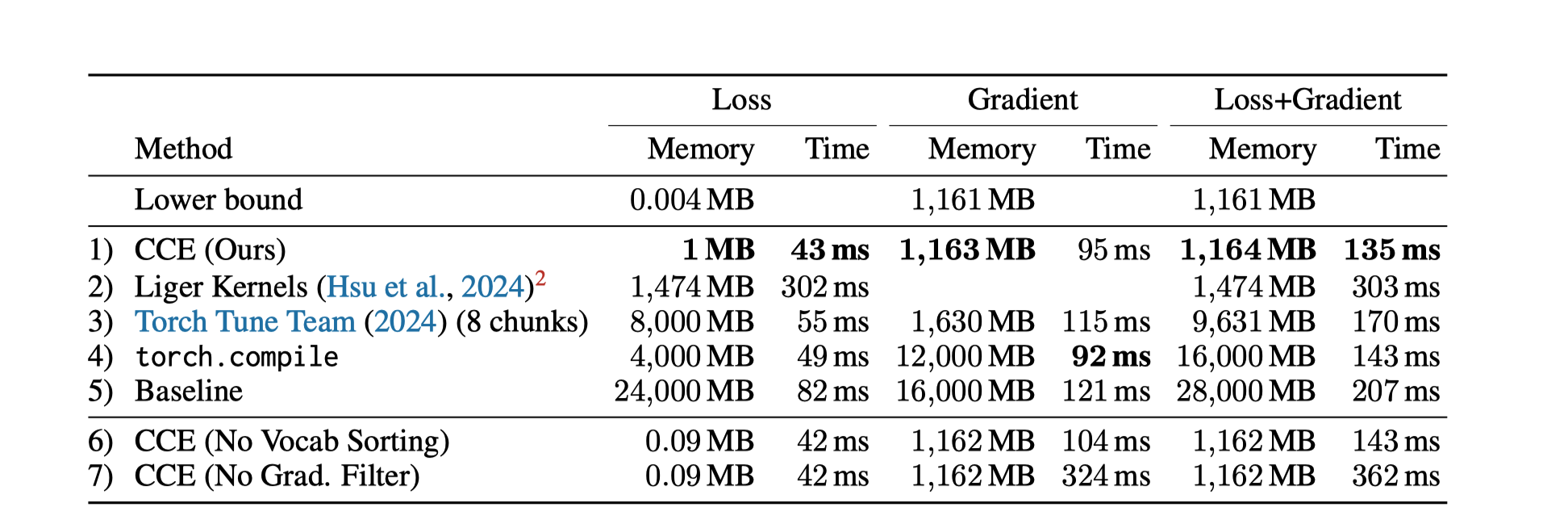
Cut cross entropy
Main idea:
- Avoid to store final large matrix throught block computation, which can save lots of memory when vocabulary is large.
Softmax matrix is sparse, when all values are smaller than precision of data type, computation are unnecessary.
Basic
Parallelization
1) Medusa
output top-k predictions for next multiple positions parallelly through adding LM heads for next several positons, which can reduce inference latency.
2) SnapKV
compress KV cacha for long sequence tasks
Infrastructure
1) triton
- An alternative language for cuda, designed for deep neural network
- published in 2019, purchase by OpenAI
- reasons why it’s great
- designed for deep neural network
- open-source, active project in Github
- clients, like unsloth, other in Github issues
- friendly to use and implentment, adding them into current Python code, Good to start
- support for other chips
2) Hardware Acceleration of LLMs: A comprehensive survey and comparison
Simple introduce and compare different hardware acceleration method in terms of efficiency and performance
- collect all method from 2020-2024
- comparison with the same process technology
- different choose for both efficiency and performance
Trick
1) Inference with Reference
Lossless Acceleration of Large Language Models: copy reference to inference because there many same text sentence between them to accelerate inference 2) SwitchHead
Accelerating Transformers with Mixture-of-Experts Attention: select different experts matrices for every head in attention by input content to reduce computation and memory usage. + published: 2024 3) DropBP:
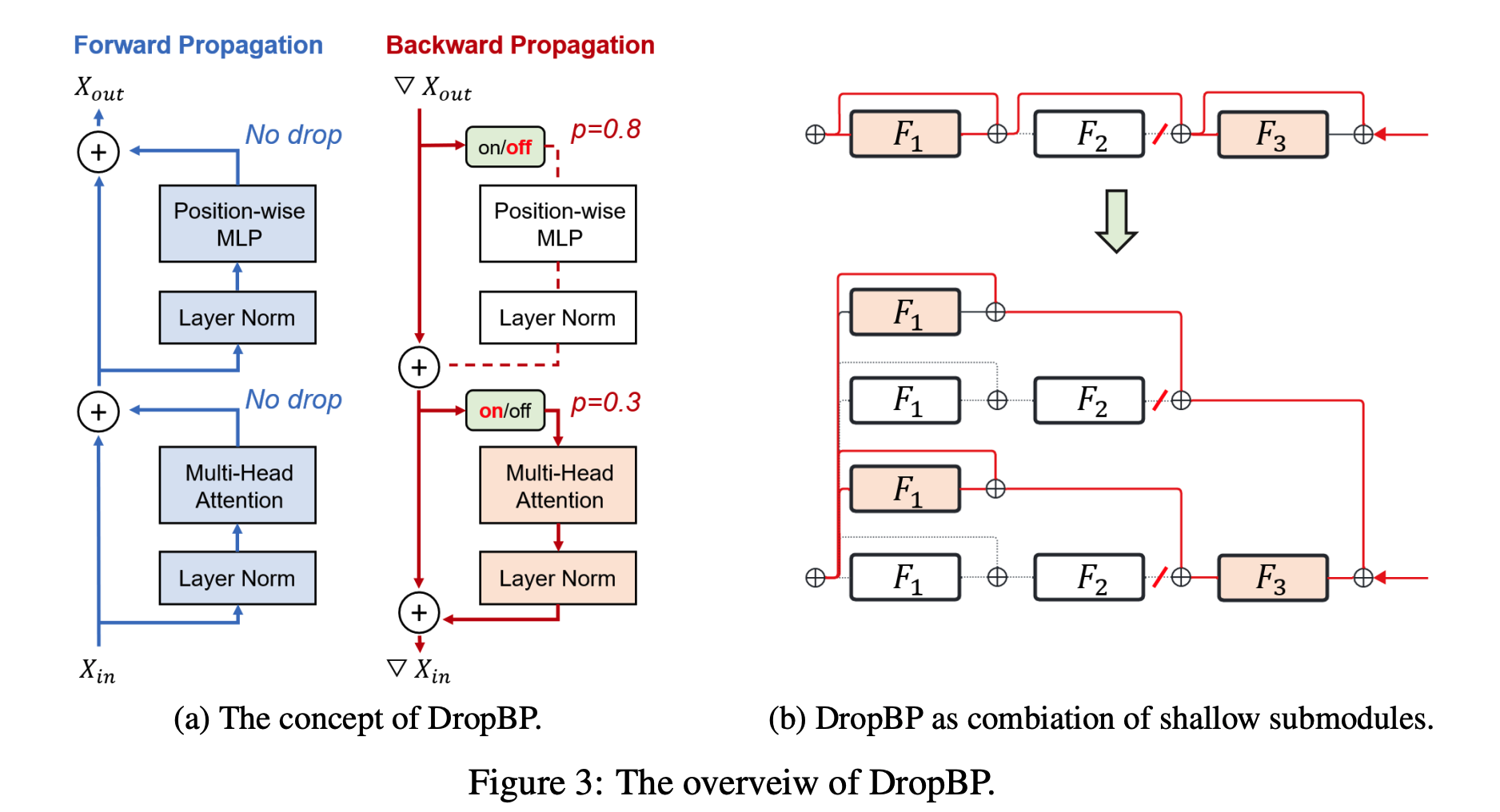
Accelerating Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models by Dropping Backward Propagation:
- Drop Backward propagation based on sensitivity which is the difference between Backward update and not update. great idea!
- change model constructure to have a 2^n submodels when drop some submodels
- published: 2024
To Read
Quantization
Optimizer
RNN
- RWKV: RWKV is an RNN with transformer-level LLM performance
Trick
Long sequence
- IceFormer: Accelerated Inference with Long-Sequence Transformers on CPUs
2:4
- Accelerating Transformer Pre-training with 2:4 Sparsity
Pruning
- Sheared LLaMA: Accelerating Language Model Pre-training via Structured Pruning
cache
- Dynamic Memory Compression: Retrofitting LLMs for Accelerated Inference
trade-off
- AWQ: Activation-aware Weight Quantization for On-Device LLM Compression and Acceleration
PE